Key Points:
- The five supplements are meant to mitigate critical aspects of aging, from dysfunctional cellular processes to reduced blood circulation.
- This article delves into the science behind Dr. Helman’s top five supplements to fight against aging.
Dr. Josh Helman is a Harvard-trained physician who primarily focuses on reversing and preventing Alzheimer’s disease. Through his research on this age-related neurodegenerative disorder, he has become an expert of sorts on aging intervention supplements. As such, in a NewsBreak press release, Dr. Helman shared his top five supplements to counteract the effects of aging. In addition to Dr. Helman’s top supplements to fight aging, this article will delve into their potential anti-aging effects as well as the science behind them.
Nitric Oxide
Nitric oxide, which is a gas at room temperature, dilates blood vessels and improves circulation. Its mechanism of action, whereby it enhances blood flow to organs and tissues, is believed to promote cellular repair and regeneration as well as improve the function of the cell’s powerhouse (known as mitochondria).
Moreover, as people age, nitric oxide production in cells that line blood vessels falters. This phenomenon leads to stiffening arteries, high blood pressure, and reduced circulation. Thus, maintaining adequate nitric oxide levels through methods such as regular exercise or supplementation with nitric oxide supplements may help mitigate these age-related aspects of cardiovascular functional deterioration. Accordingly, nitric oxide supplementation may serve as a way to promote heart function and longevity.
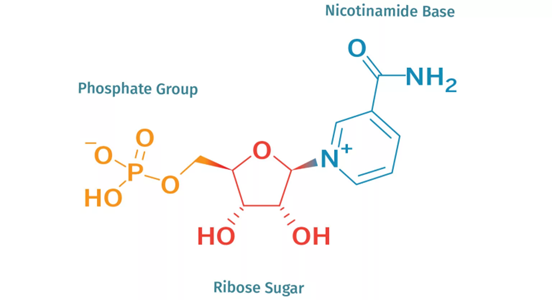
Nicotinamide Mononucleotide (NMN)
NMN increases levels of a molecule essential for various cellular processes, including energy generation, DNA repair, and metabolic regulation, known as nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+). In multiple organisms, including humans, and across different tissues, NAD+ levels have been shown to decline with age. Accordingly, a large swath of aging researchers considers falling NAD+ levels a key characteristic of aging.
Boosting NAD+ levels with NMN has been shown to suppress age-associated weight gain, enhance metabolism, improve insulin sensitivity, and alleviate the age-related functional decline of organs like the eyes and skeletal muscle in rodents. While these findings are promising, human trials testing NMN’s effects have been mixed.
Limited Evidence from Human Trials
In that regard, human trials have demonstrated that NMN supplementation increases blood concentrations of NAD+. Moreover, research also suggests that NMN improves muscle strength and performance in older men. Accordingly, human data on NMN is somewhat limited, but further studies are currently ongoing. However, some of the initial trials on NMN suggest it may help counteract certain aspects of aging in humans, such as muscle weakening.
Honokiol
Honokiol is a natural plant-derived compound found in magnolia bark, seed cones, and leaves. It is known for having various pharmacological properties, including potential neuroprotective, anti-cancer, and anti-inflammatory effects. Research also suggests that honokiol has anti-anxiety and sleep-promoting properties.
Neuroprotection
Research in rodents has shown promise in protecting against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Honokiol may help protect against these diseases with its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and mitochondria-modulating properties.
Anti-inflammation
Honokiol can inhibit certain inflammatory pathways that are involved in inflammatory diseases like Alzheimer’s disease. Moreover, with its anti-inflammatory properties, honokiol may counteract chronic, low-grade systemic inflammation, a proposed hallmark of aging.
Anti-Senescence Action
Research suggests that honokiol helps reduce the accumulation of senescent cells (cells that stop dividing but remain metabolically active and can promote inflammation) in tissues like the brain and skin.
Anti-Cancer Properties
Research using human cancer cell lines suggests that honokiol has anti-proliferative and cell death-inducing effects in many types of cancer, like prostate, breast, lung, ovarian, and colorectal cancers. These findings make honokiol a promising candidate compound for cancer prevention and treatment.
Modified Citrus Pectin
Modified citrus pectin is a soluble fiber derived from the peels of citrus fruits like lemons, limes, and oranges. Its purported effects include supporting normal cellular growth; the function of various tissues like the kidney, liver, and heart; and optimal immune function.
Modified citrus pectin’s mode of action is believed to entail binding to and aiding in the removal of toxic particles like lead, arsenic, and mercury. In this way, modified citrus pectin may help cleanse the body of toxins.
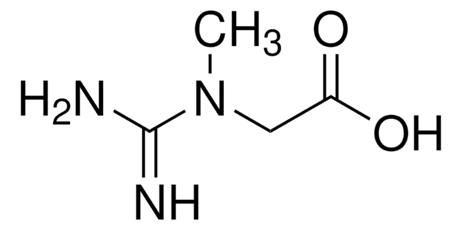
Creatine
Creatine is a molecule, naturally produced in the liver, kidneys, and pancreas. It helps regenerate ATP, the main energy source for cells. As such, creatine plays a pivotal role in the metabolism of tissues with high energy demands, such as muscles, the heart, and the brain.
Supplementing with creatine can help combat the age-related weakening of muscle and faltering muscle performance. Moreover, creatine supplementation can increase brain creatine levels, potentially improving cognitive processes and memory, particularly in older adults in times of stress. Accordingly, supplementing with creatine may help preserve physical as well as cognitive function during aging.
Dr. Helman’s Top Supplements Target Multiple Facets of Aging
With his top five supplement recommendations, Dr. Helman targets various aspects of aging, ranging from things like cardiovascular circulation to systemic detoxification and cognitive performance. For individuals who are getting older, incorporating these supplements into their daily routine may serve as a body-wide rejuvenation strategy. As the acquisition of further human data will be necessary to confirm their efficacy, the possibility looms that using these supplements may extend the number of years lived without chronic, debilitating age-related conditions.