Key Points:
- Taking NR prior to and during doxorubicin treatment helps prevent cardiotoxic effects.
- NR treatment leads to increased exercise tolerance and reduced doxorubicin-induced effects on heart function.
- Treatment with NR also leads to less scar tissue build-up with doxorubicin and better vascular response to chemical stimulants.
As we age, we are more susceptible to various maladies, including cancer. Cancer can often lead to other concerns due to not just the disease’s symptoms but also the side effects of the myriad of medications used to fight it. Doxorubicin is a strong chemotherapy agent used for multiple types of cancers, including breast cancer, bladder cancer, and lymphoma. However, it carries the possible side effect of heart failure. A new study shows that treating patients with NR may help protect their hearts from the cardiotoxic effects of doxorubicin.
The study, from scientists in Russia and published in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences, focused on male rats with doxorubicin-induced heart disease. The rats were given doxorubicin, as well as NR, either prior to doxorubicin (preventative) and/or during doxorubicin treatment (simultaneous). Podyacheva and colleagues found that combining preventative and simultaneous NR treatment had the best protective effects on the rats’ hearts and overall health. They found that both treatment approaches increased exercise tolerance and insignificant changes to heart function. Additionally, there was less fibrotic (scar) tissue formation and lower levels of reactive oxygen species with NR treatment. Overall, NR seemed to enhance rat health, with better physical activity parameters and vasculature conditions.
“The data obtained during the study can be used for further investigation into chronic doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy prevention and treatment approaches,” the scientists wrote.
NR Protects Against Doxorubicin
The scientists used 60 adult male rats and divided them into four experimental groups: control/untreated, treated with doxorubicin alone (DOX), treated with doxorubicin and NR simultaneously (NR + DOX), or treated with NR prior to and during doxorubicin treatment (NR/NR + DOX). It is well-known that many chemotherapy agents, including doxorubicin, cause weight loss, and doxorubicin in particular, is also known to cause exercise intolerance. Thus, the researchers assessed whether NR treatment could alleviate these side effects.
In this study, the researchers found no significant difference in the rats’ weight in any of the experimental groups; however, there was a difference in exercise tolerance, where the doxorubicin alone and the doxorubicin+NR groups had decreased exercise tolerance when compared to their measurements at the start of the treatment. Their exercise tolerance continued to decrease in the following two months, indicating the delayed deleterious effects of doxorubicin.
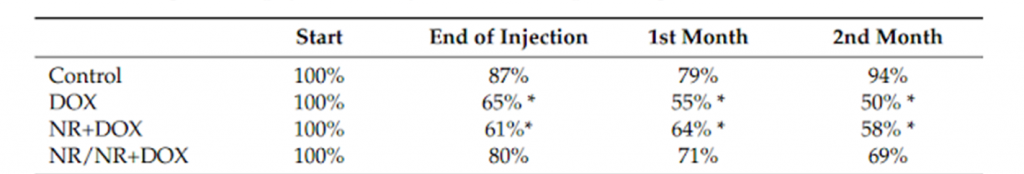
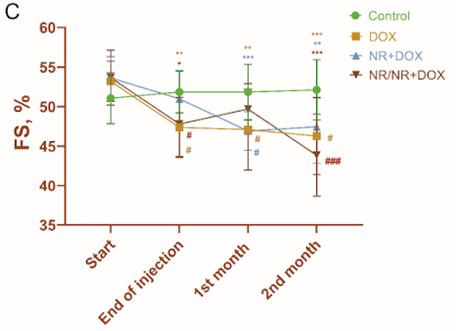
Furthermore, doxorubicin is known to cause cardiotoxicity, and the scientists looked at heart function as it relates to contraction, or pumping, of the left ventricle – the part of the heart that pumps oxygenated blood to the other organs. They found that all the treated rats had a fractional-shortening decrease – a way of assessing how well the left ventricle is contracting and pumping based on its reduction in size following the pumping phase of the heartbeat (systole). This fractional shortening decrease is indicative of impaired cardiac muscle functioning and cardiotoxicity. However, the rats treated with NR both before and during doxorubicin treatment had the least severe fractional shortening decrease, suggesting NR has protective effects.
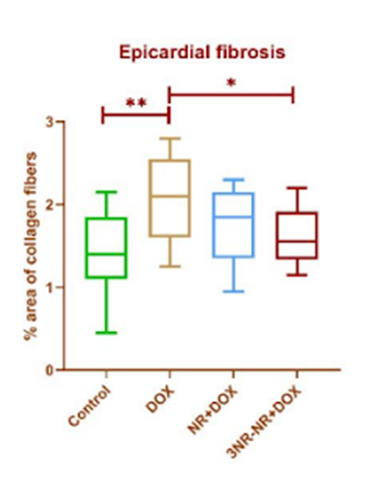
NR Attenuates Heart Fibrosis
Given the effects of doxorubicin on heart function, the researchers looked at the physical health and appearance of the heart tissue. They found increased fibrotic tissue (scar tissue) formation in the hearts of rats treated with doxorubicin alone. Fibrotic tissue is characteristic of damage to the tissue, as well as detrimental age-related changes. They also saw some fibrotic tissue in rats treated with NR, although it was less pronounced than in those treated with doxorubicin alone.
Additionally, the response of mesenteric arteries – blood vessels supplying the intestines – to different chemical stimulants was altered in the rats treated with DOX alone or NR+DOX. This data suggests that NR helps preserve the functionality and responsiveness of blood vessels further from the heart.
The scientists also looked at reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the rats’ blood two months after treatments to assess changes at the cellular level. Studies indicate that a major mechanism behind deleterious cardiac effects in various instances is increased ROS production. The researchers found that those rats treated with doxorubicin alone had the most ROS.
NR for Cardiotoxic Effects
Podyacheva and colleagues show here that NR can help reduce the cardiotoxicity effects of doxorubicin, with positive effects on heart function and at the tissue and molecular levels. Other studies have shown similar cardioprotective effects with NR treatment, such as in diabetes, due to the increase in NAD+ seen when its precursor, NR, is given. This study did not look at NAD+ levels, but the effects on ROS levels are potentially due to increased NAD+ levels.
Multiple studies have shown the positive effects of NAD+ on cases of heart failure, heart attack, and heart concerns of those with muscular dystrophy. And more than one clinical trial has looked at the effect of increased NAD+ levels due to NR supplementation in heart failure patients with various heart issues, including decreased ejection fraction (volume of blood per heart pump) and irregular heartbeat.
The evidence towards the use of NR in a cardioprotective role in both medication-induced cardiotoxicity, such as doxorubicin, and age-induced cardiac concerns is building. More clinical trials with longer-term follow-ups are required before physicians will prescribe NR for patients with heart concerns. For now, NR is available from many vitamin suppliers. As always, speak with your doctor before starting any new medications or supplements.