Key Points:
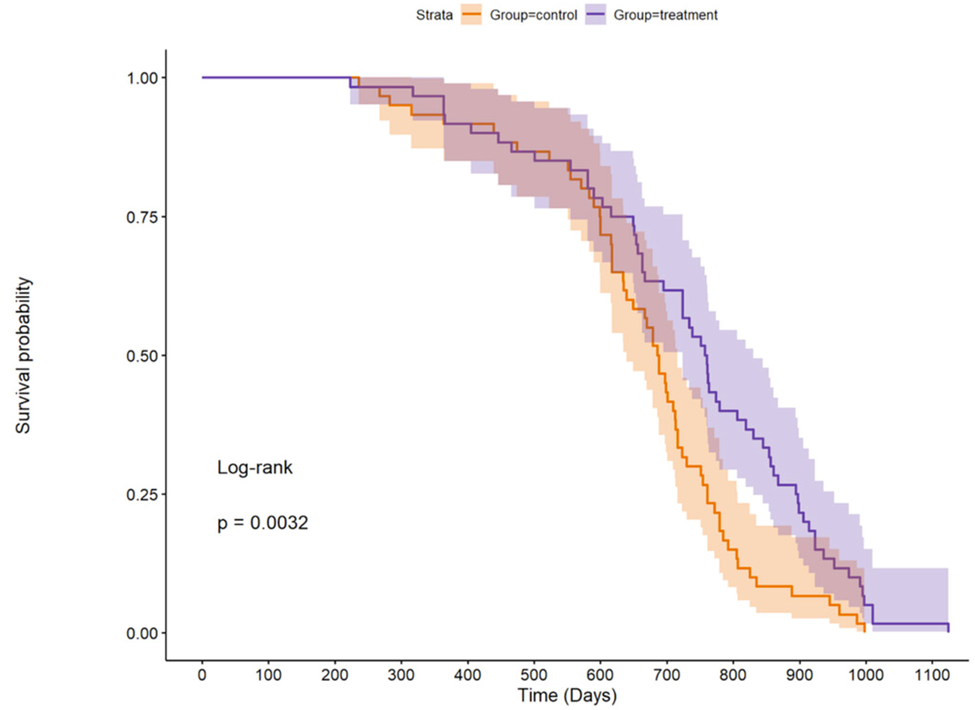
- Male mice that were administered ghrelin lived an average of 757 days, while the mice lived an average of 688 days.
- The mice that reached the 90th quantile lived for 835 days for control-fed mice and 974 days for ghrelin-fed mice.
- Regardless of treatment, for every day that the animal reached its maximum body weight later, it lived almost a whole day longer.
Researchers from the University of Alabama at Birmingham and Indiana University at Bloomington discovered that male mice given a pill made of a pharmaceutical-grade compound from a young age had a significantly longer lifespan than male mice that did not receive the pill. The pill contained an agonist for ghrelin, a molecule produced when you do not eat, and treatment of male mice from early on led to an increase in the average age of mice equivalent to 7-8 years. This molecule is believed to play a role in how calorie restriction affects the length of time a person lives. The findings were published in a peer-reviewed publication called Aging Cell.
Imitating The Effects of Calorie Restriction
Observing and implementing the beneficial effects of calorie restriction on human health and longevity has been challenging. In spite of this fact, researchers are still attempting to understand how it works by using mice models. One significant drawback of using animals as models is that they are unable to communicate with us about hunger or any other physical sensations that could shed light on the workings of the system.
A secretagogue is an agent that stimulates the production of hormones, neurohormones, chemical neurotransmitters, enzymes, or other molecules that are synthesized within cells and then secreted by those cells. Ghrelin is one such agent. There has been a significant amount of investigation into how the hormone ghrelin influences hunger, appetite, and other aspects of energy balance. Instead of reducing the amount of energy taken in, researchers studying the experiment’s effects on cognition in mouse models have hypothesized that the mechanism may be interoceptive cues—those that originate from the interior of an organism, particularly the gut and other internal organs.
In previous research, administering an oral dose of a ghrelin agonist called LY444711 to an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model reduced the disease’s pathology and improved cognitive function. At six months of age, the treatment with LY444711 decreased levels of neuroinflammation and toxic protein buildup of amyloid beta, which is a sign of Alzheimer’s disease. This was compared to the controls, but there was no noticeable difference in body weight or body fat percentage. This effect was similar to the effect seen in the group that had 20% of their calories restricted.
Ghrelin Moderately Increases Lifespan
Despite the numerous studies that have been conducted on the ways in which ghrelin influences both the amount of food consumed and the composition of the body, there has been no research conducted on the ways in which ghrelin agonists influence the length of life in rodent models. In this study, Kathryn A. Kaiser, PhD, Assistant Professor in the Department of Health Behavior at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, and her colleagues tested the hypothesis that a hunger-related pathway, such as a ghrelin agonist, would affect the lifespan of mice in a different way than it would affect the lifespan of mice that had not been treated. In this experiment, mice that were 6 weeks old were given either LY444711 or a placebo control pill and continued to be fed until they died. Animals in the treatment group had their food portions adjusted daily based on the group mean of the controls, which had been fed ad libitum for the previous week.
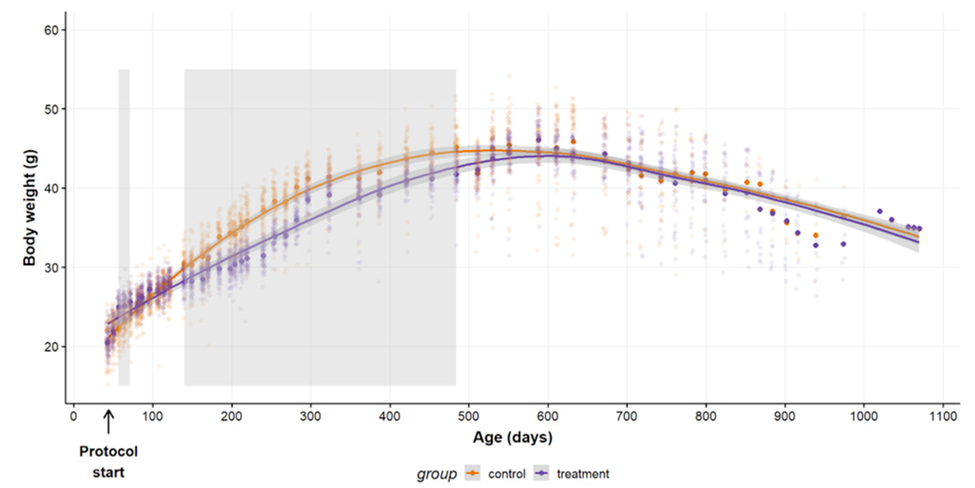
According to the findings of these experiments, exposure to the ghrelin agonist led to an increase in lifespan as well as a reduction in total body mass. The male mice that were administered ghrelin lived an average of 757 days, while the untreated mice lived an average of 688 days. This is approximately 7.67 years in human terms. The mice that reached the 90th quantile, which is the point where 90% of the data points are lower than this number, lived for 835 days for control-fed mice and 974 days for ghrelin-fed mice, which is approximately an equivalent of 15.67 human years. It was fascinating to learn that the age at which an animal reached its maximum body weight could serve as a reliable indicator of how long it would live. For every day that the animal reached its maximum body weight later, it lived almost a whole day longer, which is the same as almost 40 days.
Rat studies show that other ghrelin-related agonists have similar effects.
High-dose treatments with single agonist compounds (BIM-28131 and BIM-28125) or human ghrelin that were comparable to the compound LY444711 have been tested using rat models. These experiments resulted in an increase in fat mass, which led to an overall increase in weight gain. The only one that demonstrated a significant rise in lean mass was BIM-28131. During treatment with either BIM-28131 or ghrelin, there was an increase in food intake; however, no effects on body weight-adjusted energy expenditure were observed over the course of the 4-week study. Based on these results, BIM-28131 looks like a promising ghrelin agonist with an appealing action profile for the ghrelin agonist of catabolic diseases like cachexia, which causes the body to become weak and lose weight.
Conclusions
These observations suggest ghrelin, as a growth hormone secretagogue, may influence a network of factors related to aging or body composition. Greater focus on tissue-specific effects, neurotransmitters, gene activity, and metabolic characteristics—such as body temperature, physical activity, diet composition effects, and potential sex differences—as well as the use of composite frailty index measures are warranted.